What is Arthroscopy?
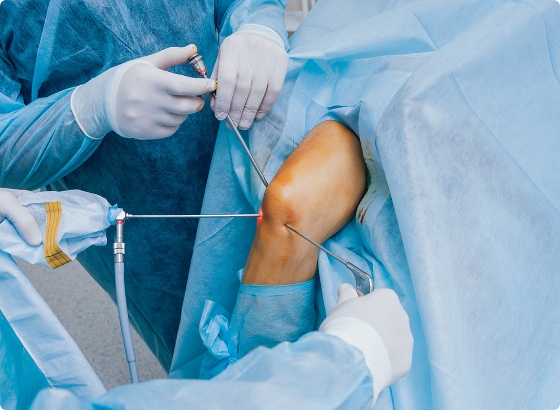
Arthroscopy literally means “to look inside a joint”. It is a type of key-hole surgery or procedure which allows the Doctors to see inside the joint. Arthroscopy is a safe, fast and effective way of diagnosing and treating problems of the joint.
How Arthroscopy is performed?
Unlike conventional “open” surgery which requires a large incision, arthroscopy is performed by making a small incision in the patient’s skin and inserting pencil-sized instruments that contain a small lens and lighting system to magnify and illuminate the structures inside the joint. Light is transmitted through fiber optics to the end of the Arthroscope that is inserted into the joint. By attaching the Arthroscope to a miniature television camera, the surgeon is able to see the interior of the joint through this very small incision. The television camera displays the image of the joint on the television screen, allowing the surgeon to look, for example, throughout the knee – at cartilage, ligaments and under the knee cap. The surgeon can determine the amount or type of injury and then repair or correct the problem if necessary.
What are the advantages of Arthroscopy?
Accuracy in identifying and dealing with the problem is the prime advantage of arthroscopy. The recovery is faster and less painful in arthroscopic surgery, as smaller incisions are made. There is minimal scar and the person can return to work or active sports very soon.
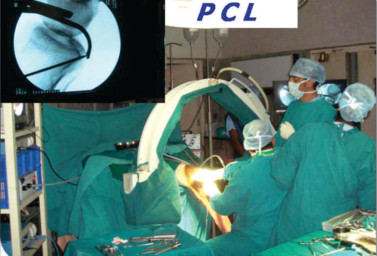
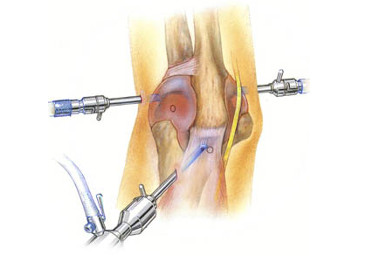
The conditions that most often require Arthroscopic surgery are
Shoulder
Recurrent dislocations
Rotator cuff tear
Impingement syndrome
SLAP tear
Elbow
Tennis elbow
Golfers elbow
Loose bodies
Synovitis
Adhesionlysis for easy stiffness
OCD
Wrist
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Triangular fibro cartilage tear
Synovitis
Hip
Femoroacetabular impingement
Loose bodies
Labral lesions
Osteonecrosis
Synovitis
Septic Arthritis
Ankle
Impingement
OCD
Arthodesis for arthritis
Instability
Knee
Meniscal tears
Cartilage defects
Anterior / posterior cruciate ligament teas
Medial patello femoral ligament tear




